Introduction to Augmented Reality
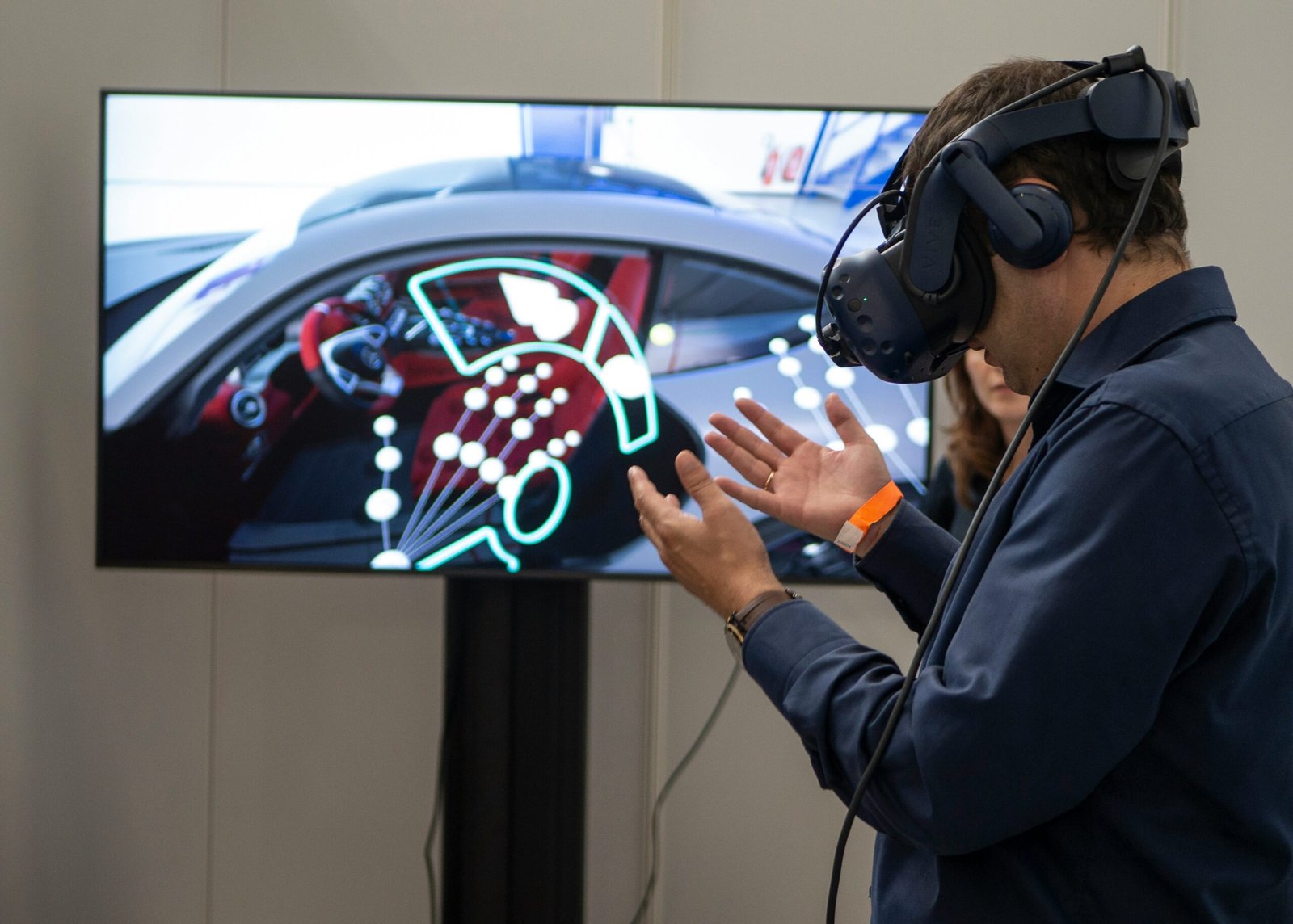
Augmented Reality (AR) is an evolving technology that enhances the real world by overlaying digital information onto physical environments. Unlike Virtual Reality (VR), which creates an entirely immersive digital experience, AR maintains a connection to reality, enriching the user’s perception without completely replacing the surrounding environment. This fundamental distinction sets AR apart, positioning it as a transformative tool across various domains.
The technology utilizes devices such as smartphones, tablets, and AR glasses to superimpose computer-generated images, sounds, and other sensory inputs onto the physical world. This creates a composite view that blends the digital and real-world elements, offering users an enriched experience that isn’t possible through traditional media. For instance, AR can enhance education by providing interactive visual aids, or it can revitalize retail experiences by allowing consumers to visualize products in their own homes before making a purchase decision.
AR has garnered attention not only in the entertainment and gaming sectors but also in fields such as healthcare, architecture, tourism, and training. In healthcare, for example, AR can assist surgeons by projecting vital information directly onto the surgical site, thereby improving precision during operations. In architecture, AR tools enable clients to visualize building projects in their proposed locations, facilitating better communication and understanding of design. Thus, while AR shares some similarities with other immersive technologies, its unique capacity to integrate digital data into real-world interactions distinguishes it as a versatile and impactful medium.
The Technology Behind Augmented Reality
Augmented Reality (AR) is defined by its ability to overlay digital information onto the real world, creating a compelling blend of physical and virtual environments. At the core of this technology are several key components that work in harmony to deliver immersive experiences. One of the fundamental technologies is computer vision, which enables devices to interpret and understand the physical space around them. Through algorithms, computer vision processes images captured by cameras, allowing devices to recognize objects, track movements, and determine the spatial relationships among various elements.
Another critical technology is Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM), which is essential for AR applications to function accurately. SLAM allows a device to create a map of an unknown environment while simultaneously keeping track of its location within that space. This is particularly vital for AR experiences that require real-time positioning and interaction with physical objects. For instance, when an AR application places a virtual object on a table, SLAM ensures that the object’s position remains consistent as users move around, providing a stable and realistic interaction.
Sensors also play a pivotal role in the efficacy of augmented reality. Various sensors, including accelerometers, gyroscopes, and depth sensors, collect data that informs the AR system about the user’s orientation and movement. By analyzing this sensor data, AR applications can adjust the placement and behavior of virtual elements, creating a seamless user experience. These technologies, when integrated effectively, enable the lifelike blending of digital and real-world components, supporting various applications in fields such as gaming, education, and retail.
In conclusion, the facilitating technologies of computer vision, SLAM, and sensors collectively empower augmented reality, fostering unique and engaging experiences that enhance our interaction with both the digital and physical worlds.
Applications of Augmented Reality
Augmented Reality (AR) is reshaping various industries by blending the digital and physical worlds, leading to innovative applications that enhance user experiences. In the gaming sector, AR has gained prominence through games like Pokémon GO, which allows players to interact with virtual creatures in real-world locations. This engagement not only enhances the gaming experience but also encourages physical activity and social interaction among players.
In education, AR applications have transformed learning environments. For instance, platforms such as Google Expeditions provide students with virtual field trips, allowing them to explore historical sites or even the depths of the ocean, all within their classroom. This immersive learning approach caters to various learning styles, engages students, and promotes retention of knowledge by providing visual and interactive elements.
The healthcare industry is also witnessing significant advancements due to AR integration. Surgeons utilize AR tools, such as Microsoft’s HoloLens, to overlay critical information onto a patient’s anatomy during procedures. This capability enhances precision and improving surgical outcomes, ultimately benefiting patient care. Furthermore, medical training programs are leveraging AR simulations to provide students with realistic practice opportunities without the risks associated with real-life surgeries.
Retail is another sector being transformed by augmented reality. Retailers like IKEA have developed AR applications that allow customers to visualize how furniture will look in their homes before making a purchase. By superimposing digital images of products onto customers’ living spaces via their smartphones, retailers can significantly enhance the shopping experience and reduce product returns. Additionally, tourism is benefiting from AR with apps that provide historical information and context to landmarks. For example, ARCity offers an interactive experience where users can point their devices at structures to reveal interesting facts and historical narratives.
In summary, the diverse applications of augmented reality across gaming, education, healthcare, retail, and tourism demonstrate its potential to enhance user engagement and improve experiences in various sectors. As AR technology continues to evolve, it promises to redefine how we interact with the world around us.
Augmented Reality in Gaming: A New Dimension
Augmented reality (AR) has significantly transformed the gaming industry, introducing an immersive dimension that enhances user engagement and interaction. One of the most notable examples is Pokémon GO, which integrates geolocation technology with AR to allow players to interact with virtual creatures in real-world settings. This innovative gameplay mechanic requires players to explore their surroundings, effectively merging the physical and digital worlds and offering a unique gaming experience.
The success of Pokémon GO can be attributed to its ability to foster community and social interaction among players. Gamers are motivated to gather at specific locations, participate in community events, and collaborate to achieve in-game objectives. This social component has far-reaching societal implications, as it encourages physical activity and outdoor engagement while also creating opportunities for people to meet and connect with each other. As players traverse parks, monuments, and urban areas, they not only engage with the game but also discover their environment in new ways.
Moreover, AR has the potential to redefine gaming mechanics themselves. Traditional gameplay is evolving as developers explore AR’s capacity to create engaging narratives that unfold in real-time based on players’ locations. This advancement allows for a more personalized experience, as the game’s challenges and rewards can be tailored to enhance immersion and drive player involvement. As AR technology continues to advance, it is expected to facilitate innovative gameplay that blurs the boundaries between the game and reality.
In light of these developments, future entertainment experiences are likely to embrace AR as a core component. The prospect of utilizing augmented reality to create interactive storytelling, multiplayer experiences, and lifelike simulations foreshadows a dynamic shift in how games are perceived and enjoyed. Therefore, the integration of AR into gaming serves as a precursor to a new era in which entertainment becomes more interactive and socially engaging.
The Role of Augmented Reality in Education
Augmented Reality (AR) is rapidly transforming the educational landscape by introducing immersive and interactive experiences that enhance learning outcomes. By overlaying digital information onto the physical world, AR provides students with a multifaceted approach to understanding complex subjects. One of the significant applications of AR in education is through interactive textbooks, which allow students to engage with the content dynamically. Instead of relying solely on traditional reading methods, students can use AR-enabled applications to access 3D models, videos, and animations that bring the material to life. This method not only enhances comprehension but also caters to various learning styles.
In addition to interactive textbooks, virtual field trips represent another innovative use of AR in education. Students can explore historical sites, scientific laboratories, or even outer space through their devices, regardless of their geographical location. This accessibility broadens students’ horizons, making it possible for learners to experience environments and phenomena that would otherwise be unattainable. Research has shown that these AR experiences lead to increased engagement and retention of information. According to a study published in the Journal of Educational Technology, students who participated in AR-enhanced learning activities scored significantly higher on retention assessments compared to those who experienced traditional teaching methods.
The effectiveness of AR in boosting student engagement cannot be overstated. Educators have reported that the use of augmented reality applications fosters a collaborative learning environment, encouraging students to participate actively in discussions and projects. By providing immediate feedback and interactive elements in lessons, AR helps demystify complex concepts, making them more accessible and enjoyable for learners. As more educational institutions adopt AR technology, its potential to revolutionize teaching methodologies and improve student learning outcomes becomes increasingly evident.
Augmented Reality in Retail: Enhancing Shopping Experiences
Augmented reality (AR) is revolutionizing the retail industry by bridging the gap between the digital and physical shopping experiences. With the implementation of AR technology, retailers are providing consumers with the ability to visualize products in their own environment before making a purchase. This capability significantly enhances the decision-making process, as customers can see how items fit and look in their personal spaces, effectively reducing the likelihood of dissatisfaction post-purchase.
One of the most notable features of AR in retail is the virtual try-on experience. Fashion retailers, for example, have adopted AR solutions that allow customers to virtually try on clothing and accessories using their mobile devices or smart mirrors. This technology provides a personalized and interactive shopping experience, enabling customers to experiment with different styles and sizes without the need to physically try on items. As a result, shoppers can gain confidence in their choices, which may lead to increased sales and customer satisfaction.
In addition to virtual try-ons, AR is also enhancing in-store navigation. Retailers are utilizing augmented reality apps to guide shoppers through large stores, effectively reducing time spent looking for products. By scanning the store layout with their smartphones, customers can receive real-time information on product locations, promotions, and even recommendations based on previous purchases. This not only streamlines the shopping process but also facilitates a more engaging and efficient interaction with the store environment.
Overall, the adoption of augmented reality in retail presents significant benefits for both consumers and businesses. By offering enhanced visualization and improved in-store experiences, retailers can create a more satisfying shopping journey. As AR technology continues to evolve, its impact on the retail landscape is poised to grow, offering new avenues for customer engagement and brand loyalty.
Challenges and Limitations of Augmented Reality
Augmented Reality (AR) is hailed as a transformative technology, yet its widespread adoption faces several challenges and limitations that must be addressed. Primarily, privacy concerns arise as AR applications often require access to extensive user data, including location and camera feeds. These requirements can lead to apprehension among users regarding how their personal information is utilized or shared, ultimately hindering the acceptance of AR. It is crucial for developers to prioritize transparent data practices and implement robust privacy policies to build user trust.
Technological limitations also pose significant hurdles for AR. Despite advancements, the quality and performance of AR applications can be inconsistent across different devices. Factors such as hardware capabilities, software compatibility, and internet connectivity can affect the user’s experience. For instance, older smartphones may struggle to efficiently support complex AR functionalities, potentially leading to lagging visuals and decreased user satisfaction. Overcoming these technological barriers necessitates ongoing investment in research and development to optimize AR applications for a wider range of devices.
User acceptance remains another critical challenge. While AR offers innovative experiences, some individuals may feel overwhelmed by the technology or skeptical about its necessity. Education and user-friendly designs are essential to enhance understanding and encourage engagement with AR applications. Providing tutorials, support, and clear value propositions can help demystify AR and stimulate interest among potential users. Furthermore, creating immersive and seamless experiences may foster greater acceptance.
In conclusion, although Augmented Reality holds immense potential, addressing privacy concerns, technological limitations, and user acceptance will be vital in fostering a positive experience that empowers users and encourages broader adoption of this innovative technology.
The Future of Augmented Reality
As augmented reality (AR) technology continues to evolve at a rapid pace, numerous trends and advancements are anticipated in the coming decade. One of the most significant predictions involves the potential integration of AR with artificial intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT). This convergence could lead to more intuitive and personalized immersive experiences, allowing users to interact with their environment in ways previously imagined only in science fiction.
The integration of AI into AR systems is poised to enhance the contextual understanding of users. For example, AR applications could leverage AI algorithms to analyze a user’s surroundings, making real-time adjustments and suggestions. This could range from providing navigational prompts during outdoor excursions to offering product recommendations while shopping. Thus, the interplay between AI and augmented reality creates a robust platform for deeper engagement and information delivery, fundamentally transforming how we consume and interact with digital content.
Moreover, the rise of the Internet of Things presents another avenue for growth. As IoT devices proliferate, the synergy between these devices and augmented reality could foster seamless connectivity in our daily routines. For instance, smart home systems may utilize AR to provide users with visual overlays that show energy consumption patterns or security footage, enhancing the user experience and facilitating more informed decision-making.
Looking further ahead, the blurring of virtual and physical realities is expected to intensify. As AR becomes more prevalent in educational, medical, and entertainment sectors, users will increasingly engage in hybrid environments that combine the digital with the tangible. This shift will prompt industries to rethink design and interaction methodologies, ultimately leading to innovative applications that redefine user experiences. As we progress into the next decade, it is evident that augmented reality will play a pivotal role in shaping the future of human-computer interaction.
Conclusion: The Transformative Power of Augmented Reality
In conclusion, augmented reality (AR) has emerged as a formidable technological advancement, reshaping the way we interact with our environments and access information. Throughout this blog post, we have explored AR’s remarkable potential across various sectors including education, healthcare, entertainment, and retail. By overlaying digital information onto the physical world, AR enhances user experiences, making them more engaging and informative. Its diverse applications demonstrate a significant shift from traditional methods to more interactive, immersive experiences.
In the realm of education, augmented reality has the ability to bring abstract concepts to life, allowing students to visualize complex ideas and engage with their learning materials in a novel way. Meanwhile, in healthcare, AR tools assist medical professionals with enhanced visualization, leading to more accurate diagnoses and improved patient outcomes. The entertainment industry also benefits greatly from augmented reality, offering users exciting, interactive content that transcends mere passive consumption and invites active participation.
Furthermore, the retail sector is being transformed as retailers adopt AR to create more immersive shopping experiences. Consumers can visualize products in their own environment before making a purchase, bridging the gap between online and offline shopping. This evolution in customer engagement is redefining the rules of commerce and altering consumer behaviors.
As we consider the implications of augmented reality technology, it becomes evident that its transformative power extends far beyond novelty. The ongoing evolution of AR is set to impact our personal and professional lives in profound ways, enhancing communication, learning, and interaction. As AR technology continues to mature, it is essential for individuals and organizations to stay informed and prepared to embrace these innovations, ultimately leading to a more enriched understanding of the world around us.